Why is my diagnosis so important?
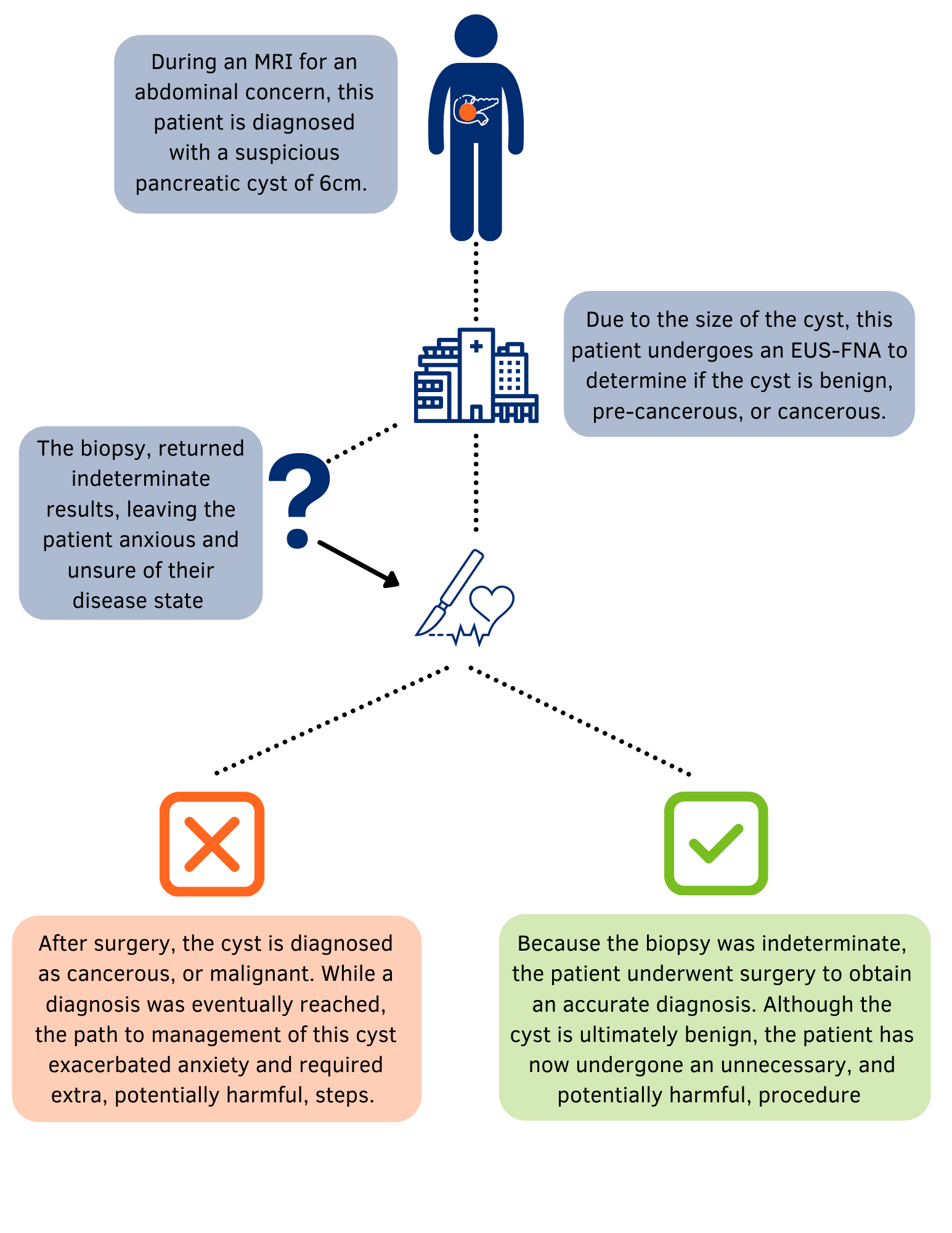
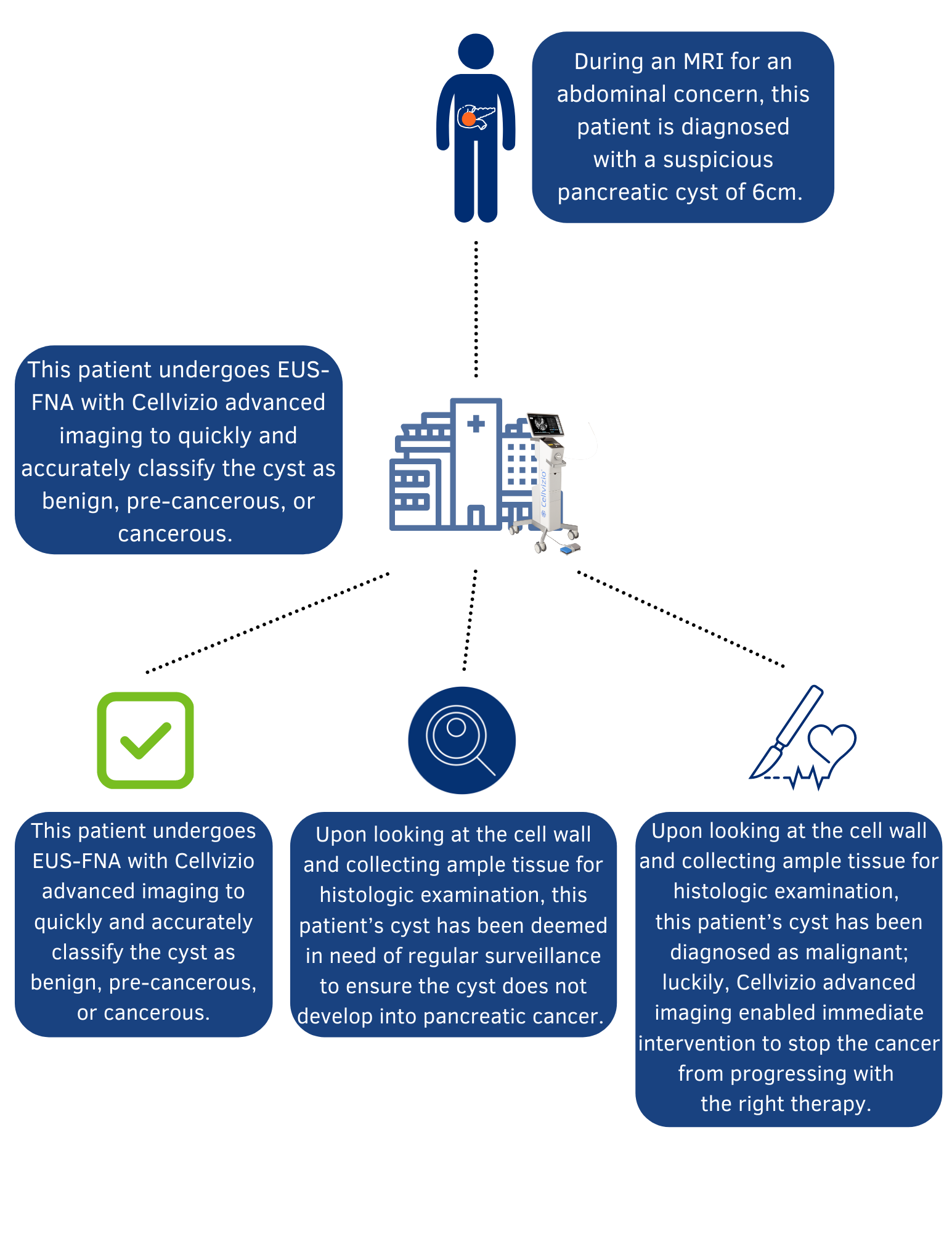
A timely and accurate diagnosis of your pancreatic cyst is essential for understanding its nature and guiding the most appropriate medical care. Once a person learns that he or she has a suspicious and previously undiagnosed pancreatic cyst, they should get an examination right away to determine if the cyst is cancerous. While not all pancreatic cysts are cancerous, it is essential to have confidence in the state of your cyst since pancreatic cancer is often found at a later stage and can spread quickly, which makes it harder to treat.
What are my diagnostic options?
The major challenge during diagnosis is to determine if a suspicious pancreatic cyst is benign, pre-cancerous, or cancerous. Certain evaluations, examinations, and tests may be done to help with the diagnosis and associated treatment plan. These can include:
- Medical History. Previous experience of abdominal injury or pancreatitis may indicate a pseudocyst (benign cyst). The characteristics and location of the pancreatic cyst, along with age and sex, can help doctors identify the type of cyst.
- CT Scan. Used to provide detailed information regarding the structure of a pancreatic cyst.
- MRI Scan. Used to highlight subtle details of a pancreatic cyst, including whether or not it has solid components.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS). Can provide a detailed image of the cyst and collect fluid for analysis in a laboratory, through a fine needle aspiration (FNA) procedure
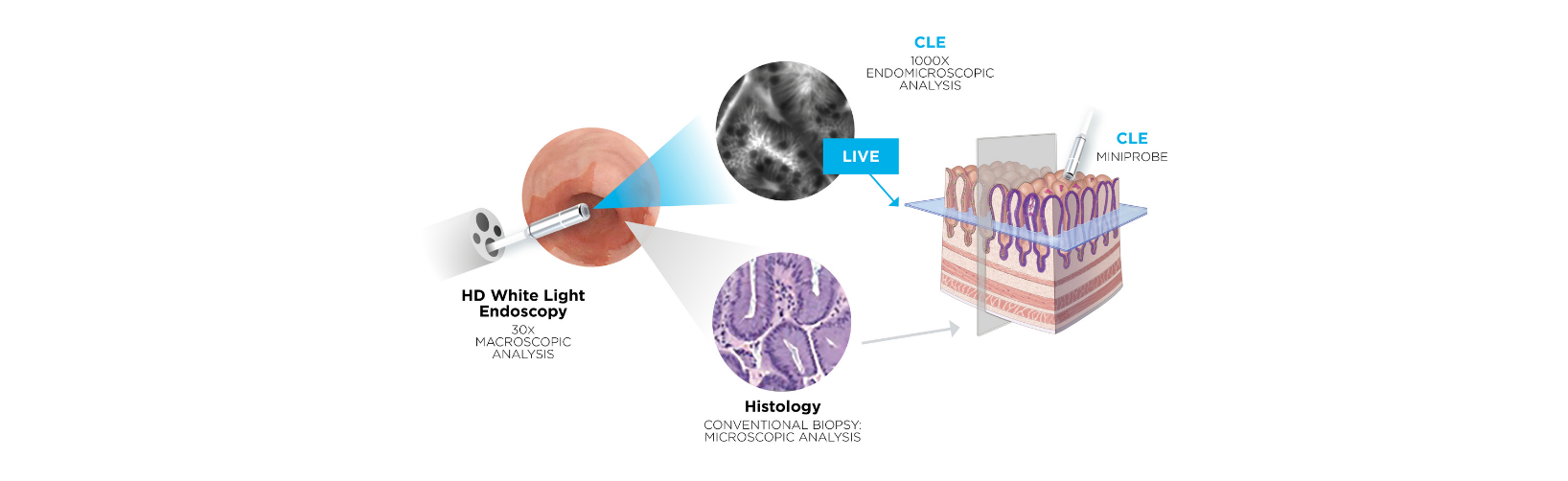
- Advanced Imaging. Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE) is an advanced imaging technology used in addition to EUS-FNA for real-time visualization of the tissue inside your body.
Following the standard of care does not guarantee the most accurate diagnosis of your pancreatic cyst; thus, exploring other methods for diagnosis, treatment, and management is essential for your health and well-being.
Advanced Imaging with Cellvizio®
Cellvizio is the real-time, in vivo cellular imaging platform. Using Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE), this technology enables physicians to accelerate diagnosis, better inform treatment, and improve therapy delivery. With 20 U.S. FDA 510(k) clearances, Cellvizio is clinically proven to be a safe and effective tool. This well tested and state of the art technology has positively impacted the lives of patients like you across the world.
Cellvizio advanced imaging enables doctors to examine tissue at the microscopic level during an endoscopic examination, facilitating traditional tissue sampling and speeding up the process between examination, diagnosis, and intervention.
When physicians examine and sample suspicious pancreatic cysts using Cellvizio, he or she is provided with real-time images that can help with tissue characterization at the time of the endoscopic examination. They can look directly at the cyst wall and collect tissue samples for a definitive biopsy, accelerating the diagnostic process and reducing patient anxiety. Using this advanced imaging technology, trained physicians may be able to make faster evaluations which have the potential to speed treatment for situations where pancreatic cancer is detected; with Cellvizio, patients can avoid unnecessary, potentially harmful, surgical procedures. Other technologies cannot deliver a definitive diagnosis with high accuracy, especially for certain benign or malignant cysts, in the way that Cellvizio can.
“We hope that, at the end of the day, we are saving lives either by diagnosing pancreatic cancer early on before it develops into cancer, or we are preventing unnecessary surgery of a benign, harmless pancreatic cyst.”
-Dr. Somashekar Krishna on the use of Cellvizio for accurately diagnosing precancerous pancreatic cysts3
Management Depends on Diagnosis
Management of pancreatic cysts varies depending upon their type and whether or not they are benign, pre-cancerous, or cancerous and on whether or not they are causing symptoms. Treatments may include:
Surveillance: All pancreatic cysts warrant monitoring with CT scans, or depending upon their stability, endoscopic ultrasound. Pseudocysts are benign cysts and may be left alone as long as they aren’t adversely affecting the patient. A serous cystadenoma (a type of benign cyst that can displace organs) rarely becomes cancerous and can be left alone unless it causes symptoms or grows.
Draining the Cyst: A benign cyst (pseudocyst or serous cystadenoma) causing bothersome symptoms or increasing in size may be drained using an endoscopic procedure with fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). The endoscope is equipped with a needle to drain the cyst and can collect the fluids and, if necessary, tissue samples to be analyzed for cancerous cells. Targeted biopsy permits cellular evaluation of the pancreatic cyst wall during the endoscopic examination. Cellvizio targeted biopsy utilizes the world’s smallest microscope and laser imaging technology as an adjunct to today’s endoscopic instruments to identify tissues at the cellular level during an endoscopic procedure.
Surgery: Surgery may be needed to remove some benign cysts: an enlarged pseudocyst or a serous cystadenoma that’s causing pain or other symptoms. Other types of pancreatic cysts generally require surgical removal because of the risk of cancer and to enable them to be fully evaluated to determine if cancer cells are present.
Watchful Waiting: Sometimes a pancreatic cystic lesion requires no further surveillance or intervention, but may be evaluated from time to time to ensure nothing has changed.
Any diagnostic assessment should always be made by the attending physician.
See if Cellvizio is Right for You
2 Rodríguez-D’Jesús A, et al. Impact of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) and EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration
on the management of pancreatic cystic lesions. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016.
3 https://wexnermedical.osu.edu/mediaroom/pressreleaselisting/pancreatic-cyst-mmr